What Is a Broker in Forex?
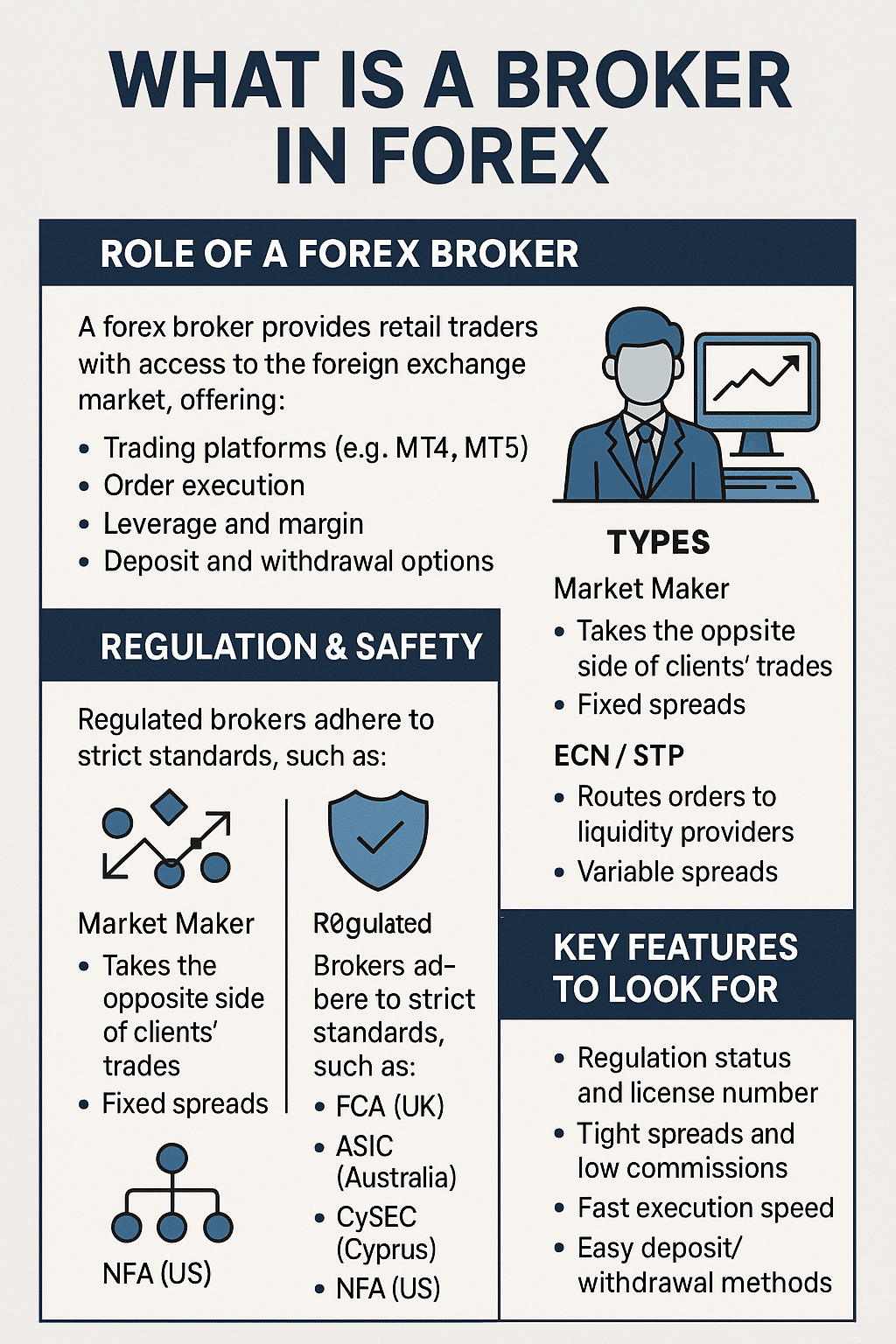
A broker in forex is a financial intermediary that allows individual traders and institutions to access the global foreign exchange market. Without a forex broker, retail traders would not be able to trade currency pairs like EUR/USD or GBP/JPY. This article explains how forex brokers operate, what types exist, how they make money, and how to choose one safely and profitably.
What Does a Forex Broker Do?
A forex broker provides a trading platform and infrastructure for clients to buy and sell currencies. Brokers connect retail clients to the forex market, either by acting as counterparties or by routing trades directly to liquidity providers.
They typically offer:
- Access to platforms like MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MT5, cTrader, or custom web terminals
- Real-time quotes for currency pairs
- Order execution and trade management tools
- Leverage, margin accounts, and risk settings
- Deposit and withdrawal infrastructure
Example in Practice
When a trader opens a buy order on GBP/USD through their broker’s MT4 platform, the broker either fills the order internally (Market Maker) or routes it to a liquidity provider (ECN/STP), depending on the model.
Types of Forex Brokers
Market Maker (Dealing Desk) Brokers
These brokers create their own internal market. They may take the opposite side of client trades, profiting when the client loses. They offer fixed spreads and guaranteed liquidity, but may have conflicts of interest.
Pros:
- No commission trading
- Often better for beginners
Cons:
- Possible conflict with trader profitability
- Requotes and slippage during volatile periods
ECN (Electronic Communication Network) Brokers
ECN brokers connect clients directly to liquidity providers. They aggregate the best bid and ask prices from multiple institutions and charge a commission per trade.
Pros:
- True market pricing
- Tighter spreads and better transparency
Cons:
- Commission-based fees
- Requires a higher level of trading experience
STP (Straight Through Processing) Brokers
STP brokers route orders to external providers without human intervention. They may add a small markup to the spread as compensation.
Hybrid Models: Many brokers today use a mix of ECN and STP execution to serve both institutional and retail clients.
How Do Forex Brokers Make Money?
Forex brokers earn revenue through:
- Spreads: The difference between bid and ask prices (e.g., EUR/USD 1.1050 / 1.1052 = 2-pip spread)
- Commission Fees: Charged per trade lot (typically $3–$7 per side)
- Swap Fees: Interest for holding positions overnight (based on currency pair interest rate differentials)
- Markup on Spreads: Especially in STP models
Some brokers also offer premium services like VPS hosting or priority withdrawal for additional fees.
Regulation and Trustworthiness
Traders must choose regulated brokers to protect their funds and ensure fair dealing. Trusted regulators include:
- FCA (UK) – Check FRN on register.fca.org.uk
- ASIC (Australia) – Regulates brokers under strict capital and compliance laws
- CySEC (Cyprus) – Common for EU brokers
- NFA/CFTC (US) – Very stringent, often limits leverage to 1:50
Red flags include:
- Unregulated brokers with high bonuses
- Withdrawal delays or blocked accounts
- Poor customer support or unverifiable contact information
Choosing the Right Forex Broker
Key Factors to Compare
- Regulation and licensing
- Execution speed and trade slippage
- Spread and commission structure
- Trading platform and tools
- Deposit and withdrawal methods
- Educational content and demo account access
Verified Tip:
Always test a broker using a demo or small live account first. TradersTrusted includes up-to-date expert reviews of brokers including Intertrader, Pepperstone, IC Markets, and more.
Real-World Case Study
In 2024, a South African trader used an unregulated broker offering 1:1000 leverage. After 3 months, he encountered withdrawal restrictions and poor execution. He later switched to an FCA-regulated broker with 1:30 leverage and transparent fees, resulting in improved trading discipline and consistent withdrawals.
Key Takeaways
- Forex brokers give retail traders access to global currency markets
- They differ in execution models: Market Maker, ECN, and STP
- Regulation is crucial to protect trader funds and ensure fairness
- Brokers earn money through spreads, commissions, and swaps
- The best brokers are licensed, transparent, and provide strong platforms and support
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of a forex broker?
A forex broker provides access to the currency market, facilitates order execution, and offers tools for trading, analysis, and account management.
How do forex brokers make money?
They make money through spreads, commissions, and overnight swap fees, depending on their execution model.
Are all forex brokers regulated?
No. Many offshore brokers operate unregulated. Only use brokers licensed by trusted authorities like the FCA, ASIC, or NFA.
What platform do most forex brokers use?
Most offer MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), cTrader, or proprietary platforms for web and mobile trading.
Can a forex broker trade against me?
Yes, Market Maker brokers can take the opposite side of your trade. ECN/STP brokers route your orders to the wider market.

