Forex Risk Management & Trading Psychology: The Complete Guide
Introduction
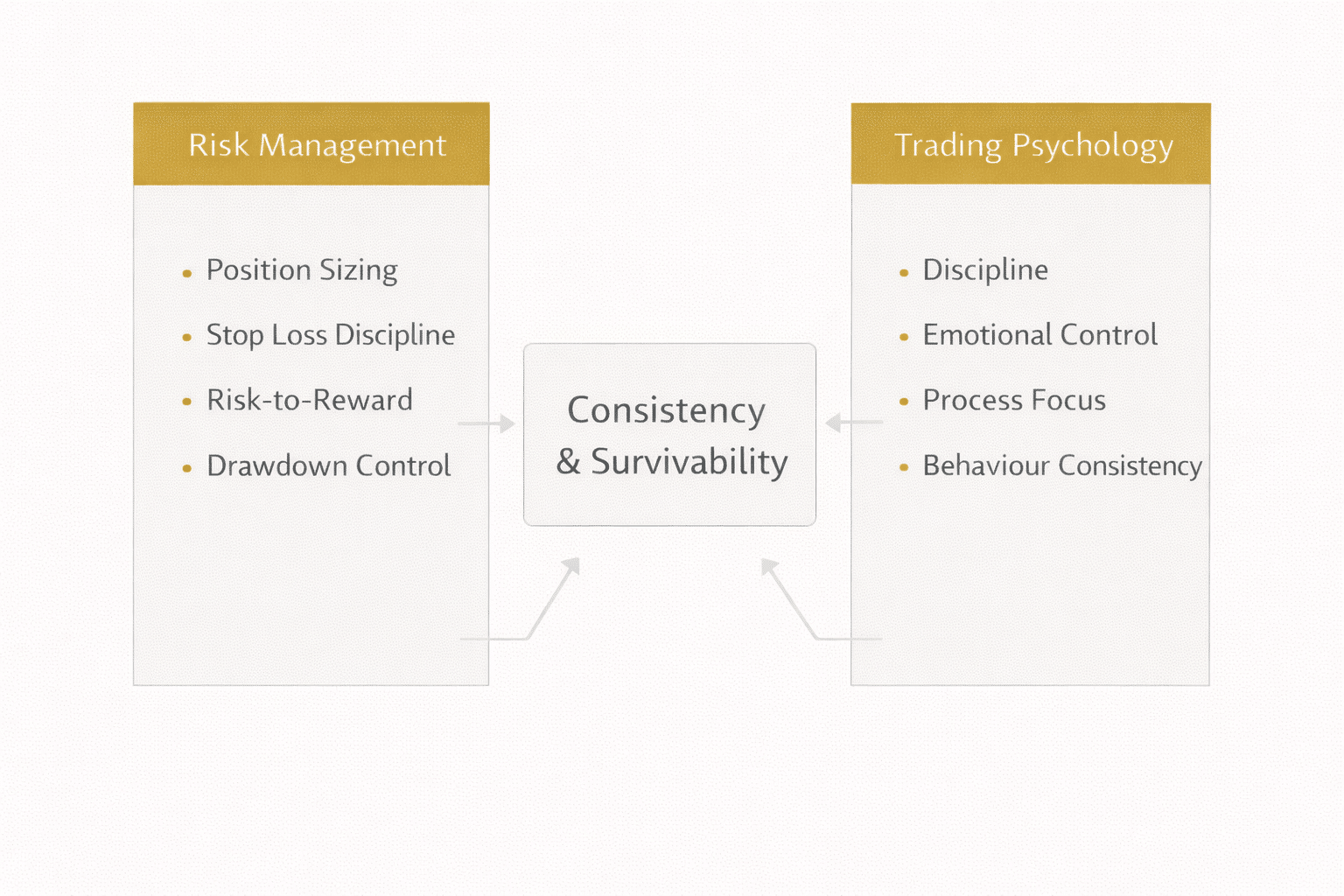
Forex risk management and trading psychology determine whether a trader survives long enough to benefit from any strategy. Most traders focus on entries, but professionals focus on downside control, behaviour, and discipline. This guide explains risk management in forex trading step by step, shows how psychology affects execution under pressure, and outlines the professional frameworks used to stay consistent across different market conditions.
Forex risk management and trading psychology are the disciplines that control losses, regulate behaviour, and ensure long-term survivability in forex trading.
What Forex Risk Management Really Means
Forex risk management is not about eliminating losses.
Losses are inevitable. Risk management exists to control how much damage any single trade, sequence of trades, or emotional lapse can cause. Professional traders design their risk framework so that no single decision can materially harm their trading capital.
In practice, risk management defines survival first, performance second.
Core Principles of Risk Management in Forex Trading
Professional risk management is simple, numerical, and non-negotiable.
Position Sizing in Forex Trading
Position sizing determines how much capital is exposed on each trade.
Professionals risk a fixed, small percentage of capital per trade, regardless of confidence or recent performance. This ensures consistency and prevents emotional scaling.
Fixed risk prevents both overconfidence after wins and panic after losses.
Stop Loss Strategy in Forex
A stop loss defines where a trade idea is invalid.
Stops are placed based on market structure or logical invalidation, not comfort. Moving or removing stops is a psychological failure, not a technical adjustment.
Consistent stop discipline is the foundation of drawdown control.
Risk-to-Reward Awareness
Risk-to-reward measures whether a trade is worth taking.
Professional traders focus on asymmetric outcomes, where potential reward outweighs predefined risk. High win rates are unnecessary when losses are controlled and winners are allowed to develop.
Drawdown Management
Drawdown management protects both capital and psychology.
Professionals define maximum drawdown limits that trigger reduced size or temporary inactivity. This prevents emotional spirals and performance collapse during losing periods.
Trading Psychology in Forex: The Human Risk
Trading psychology governs behaviour under pressure.
Even perfect risk rules fail if behaviour is inconsistent. Psychology determines whether rules are followed when fear, ego, and uncertainty are present.
Markets repeatedly exploit emotional weaknesses.
Fear, Loss Aversion, and Hesitation
Fear causes traders to hesitate on valid setups and cut winners early.
Loss aversion leads to holding losing trades longer than planned. Both behaviours distort risk-to-reward and undermine long-term expectancy.
Overconfidence and Revenge Trading
After wins, traders often increase risk unjustifiably.
After losses, revenge trading seeks emotional relief rather than rational execution. Both behaviours amplify drawdowns and erode discipline.
Process Over Outcome
Professional traders judge performance by execution quality, not individual results.
A good trade can lose. A bad trade can win. Consistency comes from following process over a large sample, not reacting to outcomes.
A Professional Forex Risk Management Workflow
Step 1: Define Maximum Risk Per Trade
Set a fixed percentage risk that never changes based on confidence or emotions.
Step 2: Structure Risk Before Entry
Stop loss, position size, and invalidation must be defined before any trade is placed.
Step 3: Execute Without Adjustment
Once in a trade, follow the plan. No impulsive changes based on fear or hope.
Step 4: Monitor Drawdown, Not Individual Trades
Equity curve and drawdown limits matter more than single wins or losses.
Step 5: Review Behaviour, Not Just Results
Post-trade reviews focus on rule adherence, emotional control, and decision quality.
Risk Management vs Strategy in Forex Trading
Strategy quality matters far less than risk control.
A simple strategy with strong risk management outperforms complex systems with poor discipline over time. This is why institutional traders prioritise risk frameworks above setups.
Why Trading Psychology Determines Long-Term Consistency
Forex trading is a behavioural game.
Markets continuously test patience, discipline, and emotional stability. Traders who master psychology develop emotional neutrality, resilience, and consistency, allowing their edge to compound over time.
Common Mistakes in Forex Risk Management and Psychology
Common errors include risking too much per trade, moving stops, increasing size after losses, ignoring drawdown limits, and judging success by single outcomes.
These are psychological failures disguised as technical decisions.
Who Forex Risk Management and Trading Psychology Is For
This framework is essential for:
- Beginners seeking survival
- Intermediate traders stuck in drawdown cycles
- Advanced traders scaling capital
- Anyone trading real money
It is irrelevant only to those treating trading as entertainment.
FAQs
What is forex risk management?
Forex risk management is the process of controlling losses through position sizing, stop placement, and drawdown limits to ensure long-term survivability.
Why is trading psychology important in forex trading?
Trading psychology determines whether traders follow their rules under pressure. Without discipline, even good strategies fail.
How much should I risk per forex trade?
Professional traders typically risk a small, fixed percentage of capital per trade to control drawdowns and emotional stress.
Is risk management more important than strategy in forex?
Yes. Strong risk management and discipline matter more than strategy selection for long-term consistency.
Can good psychology compensate for a weak strategy?
Over time, disciplined behaviour and risk control can outperform poor psychology even with a simple strategy.
